Harmonious Melodies: Embarking on a Magical Journey through the World of Musicals
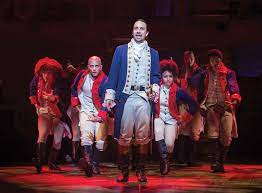
The Magical World of Musicals: A Harmonious Journey into the Heart of Theatre
When it comes to captivating audiences and creating unforgettable experiences, few art forms can match the sheer magic of musicals. From the enchanting melodies to the intricate choreography, musical theatre has a way of transporting us to another realm, where emotions are heightened and stories are told through song.
Musicals have a rich history that dates back centuries. Originating from ancient Greek theatre and evolving through various forms such as operettas and vaudeville, they have become a beloved genre that continues to thrive today. With their blend of music, dance, acting, and storytelling, musicals offer a unique and immersive theatrical experience.
One of the defining features of musicals is their ability to convey emotions in a way that words alone cannot. The power of music allows characters to express their deepest feelings and desires, taking us on an emotional rollercoaster ride. Whether it’s the soaring ballads that tug at our heartstrings or the energetic ensemble numbers that make us want to dance along, musicals have an uncanny ability to touch our souls.
Moreover, musicals provide an escape from reality. They transport us to different times and places, inviting us into worlds filled with wonder and imagination. From historical settings like 19th-century France in Les Misérables to fantastical realms like Oz in The Wizard of Oz, these productions allow us to suspend disbelief and embark on extraordinary journeys alongside the characters.
Musicals also serve as a platform for social commentary. Through clever lyrics and thought-provoking narratives, they tackle important issues such as love, justice, equality, and human nature itself. Shows like Hamilton shed light on forgotten historical figures while exploring themes of ambition and legacy. Meanwhile, Wicked challenges our perceptions by reimagining the backstory of iconic characters from The Wizard of Oz.
The impact of musicals extends far beyond their time on stage. They have the power to bring communities together, fostering a sense of unity and shared experience. Whether it’s a local production in a small town or a grand spectacle on Broadway, the communal nature of attending a musical creates a bond between audience members, as they laugh, cry, and applaud together.
In recent years, musicals have also gained popularity through film adaptations, reaching wider audiences around the world. Movies like Les Misérables and The Greatest Showman have introduced new generations to the magic of musical theatre, further solidifying their place in popular culture.
So next time you find yourself in need of an extraordinary experience that will transport you to another world, consider immersing yourself in the enchanting realm of musicals. Whether you’re drawn to classic productions like The Phantom of the Opera or eager to explore contemporary gems like Dear Evan Hansen, there is a musical out there waiting to captivate your heart and leave you humming its tunes long after the curtain falls. Let the melodies sweep you away on a harmonious journey into the heart of theatre.
8 Common Questions About Music: Answers and Resources for Music Enthusiasts in the UK
- What is the best way to learn music?
- How can I improve my musical skills?
- What are the different types of musical instruments?
- Where can I find sheet music for a particular song?
- How do I read musical notation?
- What is the difference between classical and popular music?
- How do I start composing my own music?
- What are some good books or websites for learning about music theory?
What is the best way to learn music?
The best way to learn music varies depending on individual preferences and learning styles. However, here are some general approaches that can help anyone embark on a fulfilling musical journey:
- Find your motivation: Determine why you want to learn music. Whether it’s for personal enjoyment, self-expression, or a professional career, having a clear motivation will drive your commitment and focus.
- Choose an instrument: Select an instrument that resonates with you. Consider factors such as personal interest, accessibility, and the type of music you enjoy. Popular choices include piano, guitar, violin, drums, and voice.
- Seek guidance from a teacher: Enlist the help of a qualified music teacher or instructor who can provide structured lessons tailored to your skill level and goals. A teacher will guide you through proper technique, theory, and musical interpretation while providing valuable feedback.
- Practice regularly: Consistent practice is key to improving your musical skills. Set aside dedicated practice time each day or week and establish a routine that works for you. Focus on developing technique, learning new pieces or songs, and reinforcing concepts taught in lessons.
- Study music theory: Understanding the fundamentals of music theory can greatly enhance your musical abilities. Learn about notation, scales, chords, rhythm patterns, and other elements that form the building blocks of music.
- Listen actively: Immerse yourself in various genres of music and actively listen to different artists and performers. Pay attention to melody lines, harmonies, rhythms, dynamics, and overall musical structure. This will expand your musical vocabulary and inspire creativity.
- Join a musical community: Engage with other musicians by joining bands, choirs, ensembles or attending jam sessions or open mic nights in your area. Collaborating with fellow musicians can provide valuable opportunities for growth and development.
- Embrace technology: Utilize technology to enhance your learning experience. There are numerous online resources available such as tutorials, educational websites, and apps that offer interactive lessons, sheet music, and practice tools.
- Attend live performances: Witnessing live music performances can be inspiring and educational. Attend concerts, recitals, or music festivals to observe skilled musicians in action and gain insights into performance techniques.
- Stay motivated and have fun: Learning music should be an enjoyable experience. Celebrate your progress along the way and set achievable goals to keep yourself motivated. Explore different genres, experiment with improvisation, and allow yourself the freedom to express your own musical ideas.
Remember that learning music is a lifelong journey, so be patient with yourself and embrace the process. With dedication, practice, and a love for music, you can develop your skills and find joy in creating beautiful melodies.
How can I improve my musical skills?
Improving musical skills requires dedication, practice, and a willingness to continuously learn and grow. Here are some tips to help you on your journey:
- Take lessons: Consider taking formal lessons from a qualified music teacher or instructor. They can provide guidance, correct technique, and help you develop a solid foundation in music theory and performance skills.
- Practice regularly: Consistent practice is key to improving your musical skills. Set aside dedicated time each day or week to practice your instrument or vocal exercises. Regular practice helps build muscle memory, improves technique, and enhances overall proficiency.
- Set goals: Establish specific goals for yourself, whether it’s learning a particular song, mastering a challenging technique, or improving your sight-reading abilities. Setting achievable goals provides focus and motivation for your practice sessions.
- Learn music theory: Understanding the fundamentals of music theory can greatly enhance your musical abilities. Study concepts such as scales, chords, rhythm, and harmony to deepen your understanding of how music works.
- Expand your repertoire: Explore different genres and styles of music to broaden your musical horizons. Learning diverse pieces exposes you to new techniques and challenges that can help you grow as a musician.
- Perform in public: Seek opportunities to perform in front of others, whether it’s at open mic nights, school recitals, or community events. Performing live helps build confidence and stage presence while allowing you to showcase your skills.
- Collaborate with others: Joining a band, choir, or ensemble provides valuable experience in playing with others and developing teamwork skills. Collaborating with fellow musicians allows for creative exchange and can inspire new ideas.
- Record yourself: Use technology to record yourself playing or singing so that you can listen back objectively and identify areas for improvement. Self-assessment is an effective tool for honing your musical skills.
- Seek feedback: Don’t be afraid to seek feedback from experienced musicians or teachers. They can offer constructive criticism and valuable insights that can help you refine your technique and musicality.
- Stay inspired: Surround yourself with music that inspires you. Attend concerts, listen to a variety of genres, and explore the works of influential musicians. Inspiration fuels passion and motivates you to continue improving.
Remember, improving musical skills is a journey that requires patience and perseverance. Embrace the process, enjoy the music-making experience, and never stop seeking opportunities to learn and grow as a musician.
What are the different types of musical instruments?
Musical instruments come in a wide variety of types, each producing unique sounds and playing roles in different musical traditions. Here are some of the main categories of musical instruments:
String Instruments: These instruments produce sound by vibrating strings. Examples include the guitar, violin, cello, double bass, harp, and ukulele.
Woodwind Instruments: These instruments generate sound through the vibration of air within a tube or through reeds. Common woodwind instruments include the flute, clarinet, saxophone, oboe, and bassoon.
Brass Instruments: Brass instruments create sound by buzzing the lips into a cup-shaped mouthpiece. Trumpet, trombone, French horn, tuba, and cornet are popular examples of brass instruments.
Percussion Instruments: These instruments produce sound through striking or shaking. They can be further categorized into two types:
– Pitched Percussion: Examples include the piano, xylophone, marimba, timpani (kettle drums), and glockenspiel.
– Unpitched Percussion: Examples include drums (snare drum, bass drum), cymbals (crash cymbals), tambourine, triangle, and shakers.
Keyboard Instruments: These instruments have keys that produce sound when pressed or struck. The piano is a well-known keyboard instrument along with others like organ and synthesizer.
Electronic Instruments: These instruments use electronic circuitry to generate sounds electronically. Synthesizers and electronic keyboards fall under this category.
Brasswinds: This category includes instruments that are similar to brass but have a wider conical bore shape instead of cylindrical tubing like brass instruments do. Euphoniums and saxhorns are examples of brasswinds.
Plucked Instruments: These instruments produce sound by plucking or strumming strings with fingers or picks. Examples include the guitar, banjo, mandolin, and harpsichord.
Keyboard Percussion: This category includes instruments like the vibraphone and marimba, which combine elements of percussion and keyboard instruments.
Ethnic and Folk Instruments: These are instruments specific to certain cultures or regions, such as the sitar from India, bagpipes from Scotland, djembe from West Africa, or didgeridoo from Australia.
These categories provide a general overview of musical instruments, but there are many variations and hybrid instruments that exist as well. Each instrument brings its own unique character to the world of music, enriching our auditory experiences in countless ways.
Where can I find sheet music for a particular song?
Finding sheet music for a particular song can be a thrilling adventure. There are several resources available both online and offline that can help you locate the sheet music you’re looking for. Here are some popular options:
- Music Stores: Local music stores often carry a wide selection of sheet music for various instruments and genres. Visit a nearby store and inquire about the specific song you’re interested in.
- Online Retailers: Websites such as Amazon, Sheet Music Plus, and Musicnotes offer an extensive collection of sheet music that can be purchased and delivered either physically or digitally.
- Public Libraries: Many public libraries have a dedicated section for sheet music where you can borrow or make copies of scores. Check with your local library to see if they have the song you need.
- Online Sheet Music Databases: Websites like IMSLP (International Music Score Library Project) provide free access to a vast collection of public domain sheet music, including classical compositions.
- Social Media Groups and Forums: Joining online communities or forums dedicated to musicians and sheet music enthusiasts can be helpful in finding specific songs. Members often share resources, recommendations, or even offer assistance in locating hard-to-find sheet music.
- Music Schools and Universities: If you have access to a college or university campus with a music department, their library might house an extensive collection of sheet music that is available for public use.
- Composer or Publisher Websites: Some composers or publishers maintain their own websites where they offer their original compositions or arrangements for purchase or download.
Remember, when searching for specific songs, it’s essential to include details such as the title, composer/artist name, and any relevant identifying information to increase your chances of finding accurate results.
How do I read musical notation?
Reading musical notation may seem daunting at first, but with a little practice and guidance, it becomes an accessible and rewarding skill. Here are some essential steps to help you get started:
- Familiarize Yourself with the Staff: The staff consists of five horizontal lines and four spaces. Notes are placed on the lines and in between the spaces to represent different pitches.
- Learn the Clefs: The most common clefs are the treble clef (used for higher-pitched instruments like the piano, violin, or flute) and the bass clef (used for lower-pitched instruments like the cello or bass guitar). Each clef indicates which notes correspond to specific lines or spaces on the staff.
- Understand Note Durations: Notes represent both pitch and duration. The most common note durations include whole notes, half notes, quarter notes, eighth notes, and sixteenth notes. These durations indicate how long each note should be held or played.
- Recognize Rests: Rests indicate periods of silence in music. They have durations similar to notes but are represented by specific symbols that correspond to their duration.
- Learn Key Signatures: Key signatures indicate which set of pitches (scale) a piece of music is based on. They consist of sharps (#) or flats (♭) placed at the beginning of each staff line to denote which notes should be raised or lowered throughout the piece.
- Understand Time Signatures: Time signatures tell you how many beats are in each measure and what type of note receives one beat. The top number represents the number of beats per measure, while the bottom number indicates which type of note receives one beat (e.g., 4/4 means there are four beats per measure, with a quarter note receiving one beat).
- Study Dynamics and Articulation Marks: Musical notation also includes symbols that indicate dynamics (loudness or softness) and articulation (how a note should be played, e.g., staccato or legato). Familiarize yourself with these symbols to accurately interpret the desired expression in the music.
- Practice Sight-Reading: Sight-reading is the ability to read and play music on sight without prior rehearsal. Start with simple melodies and gradually progress to more complex pieces. Regular practice will improve your reading skills over time.
Remember, learning to read musical notation is an ongoing process. Start with the basics and gradually build your knowledge as you encounter different musical pieces. Consider seeking guidance from a music teacher or using online resources that provide interactive lessons and exercises to help you develop your reading skills further. With dedication and practice, you’ll become more proficient at reading musical notation and unlock a whole new world of musical expression.
What is the difference between classical and popular music?
Classical and popular music are two distinct genres that differ in various aspects, including their historical origins, composition styles, performance traditions, and intended audience. Here are some key differences between classical and popular music:
- Historical Origins: Classical music refers to the music composed during the Classical era (1750-1820) and earlier periods, including Baroque and Romantic. It encompasses works by renowned composers such as Bach, Mozart, Beethoven, and Brahms. On the other hand, popular music emerged in the 20th century and includes genres like rock, pop, jazz, hip-hop, country, and electronic dance music.
- Composition Styles: Classical music typically follows complex compositional techniques with structured forms like sonatas, symphonies, concertos, and operas. It often features intricate melodies, harmonies, counterpoint (the interplay of multiple melodic lines), and orchestral arrangements. Popular music tends to have simpler melodies and harmonies with repetitive chord progressions that are catchy and easily memorable.
- Performance Traditions: Classical music is often performed by trained musicians in formal settings such as concert halls or opera houses. These performances may involve orchestras or chamber ensembles accompanied by professional soloists or vocalists. In contrast, popular music is commonly performed by singers or bands in various venues ranging from small clubs to large stadiums.
- Notation vs Improvisation: Classical music heavily relies on written musical notation for precise interpretation by performers. Composers specify dynamics (volume), articulation (how notes are played), tempo (speed), and other details in their compositions. Conversely, popular music often incorporates improvisation where musicians create or embellish melodies on the spot within a given framework.
- Audience Appeal: Classical music has historically been associated with a more elite or educated audience due to its perceived sophistication and cultural significance. It is often regarded as art for art’s sake rather than for commercial appeal. Popular music, on the other hand, aims to entertain a broader audience and often reflects contemporary trends, cultural movements, or personal expressions. It is typically more accessible and commercially driven.
- Commercialization: Popular music is closely tied to the music industry, with artists releasing albums, singles, and performing concerts to generate revenue. It is heavily influenced by market trends and consumer demand. Classical music, although it has its own market through recordings and performances, generally relies less on commercial success and more on grants, sponsorships, or public funding.
It’s important to note that these differences are not absolute rules but rather generalizations that help distinguish between the two genres. Over time, there has been a blurring of boundaries as composers and musicians draw inspiration from both classical and popular music traditions, creating hybrid styles that defy categorization.
How do I start composing my own music?
Embarking on the journey of composing your own music is an exciting and rewarding endeavor. Whether you’re a beginner or already have some musical knowledge, here are some steps to help you get started:
- Define your musical style and goals: Think about the type of music you want to create. Are you interested in classical compositions, pop songs, electronic music, or something entirely unique? Clarifying your musical style and goals will give you a direction to focus on.
- Learn music theory: While not mandatory, having a basic understanding of music theory can greatly enhance your composition skills. Familiarize yourself with concepts such as scales, chords, rhythm, and melody. This knowledge will provide a solid foundation for your compositions.
- Experiment with different instruments: If you play an instrument or have access to one, start exploring its capabilities and experiment with different sounds and techniques. If you don’t play an instrument, consider using digital audio workstations (DAWs) that allow you to create music using virtual instruments.
- Start with simple melodies or chord progressions: Begin by creating simple melodies or chord progressions that resonate with you. Play around with different combinations until you find something that catches your ear. Don’t be afraid to experiment and trust your instincts.
- Structure your composition: Once you have a basic idea or motif, start thinking about the structure of your composition. Decide how many sections (verse, chorus, bridge) it will have and how they will flow together. Consider dynamics (loudness/softness) and tempo changes to add depth and variety.
- Add harmony and counterpoint: Expand on your melody by adding harmonies or counterpoint lines that complement the main theme. Experiment with different chords or harmonizing techniques to create interesting textures within your composition.
- Develop your arrangement: Explore different instrumentation options for each section of your composition. Consider which instruments or sounds best convey the emotions or atmosphere you want to create. Experiment with layering different elements to add depth and complexity.
- Experiment with rhythm and dynamics: Play around with rhythm patterns, syncopation, and different tempos to give your composition a unique feel. Additionally, explore how dynamics (volume changes) can enhance the emotional impact of your music.
- Embrace improvisation: Don’t be afraid to improvise while composing. Sometimes the best ideas come spontaneously when you let yourself explore different musical possibilities without constraints.
- Seek feedback and revise: Share your compositions with trusted friends, musicians, or teachers who can provide constructive feedback. Consider their suggestions and make revisions as needed. Remember that composing is an ongoing process of learning and growth.
Most importantly, enjoy the process of creating music. Allow yourself to be inspired by various sources, experiment with different techniques, and let your creativity guide you. Composing music is a personal expression, so trust your instincts and have fun exploring the limitless possibilities of your own musical creations.
What are some good books or websites for learning about music theory?
When it comes to learning about music theory, there are several excellent books and websites available to help you deepen your understanding. Here are some recommendations:
- “Tonal Harmony” by Stefan Kostka and Dorothy Payne: This comprehensive textbook is widely used in university music programs. It covers everything from the basics of notation to advanced harmonic concepts, making it suitable for beginners and more experienced musicians alike.
- “The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Music Theory” by Michael Miller: If you’re new to music theory, this book provides a friendly and accessible introduction. It covers essential topics such as scales, chords, rhythm, and notation in an easy-to-understand manner.
- “How to Read Music: Fundamentals of Music Notation Made Easy” by Roger Evans: This book focuses specifically on reading sheet music. It offers a step-by-step approach to understanding musical notation, making it an excellent resource for beginners.
- “Music Theory for Dummies” by Michael Pilhofer and Holly Day: Similar to other books in the “For Dummies” series, this guide presents music theory concepts in a straightforward and engaging manner. It covers topics such as scales, intervals, chords, and composition.
- musictheory.net: This website offers interactive lessons, exercises, and tools for learning music theory online. It covers a wide range of topics including reading sheet music, identifying intervals and chords, understanding key signatures, and more.
- teoria.com: Another valuable website for learning music theory is teoria.com. It provides lessons on various aspects of music theory along with interactive exercises that allow you to practice what you’ve learned.
- Coursera.org: Coursera offers online courses on various subjects, including music theory. You can find courses from renowned institutions like Berklee College of Music or the University of Edinburgh that cater to different levels of expertise.
Remember that while books and websites can provide a solid foundation, it’s also beneficial to apply what you’ve learned by playing an instrument, analyzing music, and engaging in practical exercises. Combining theory with hands-on experience will help you develop a well-rounded understanding of music.
Tags: ancient greek theatre, another realm, art forms, beloved genre, blend of music dance acting storytelling, captivating audiences, creating unforgettable experiences, emotions heightened, enchanting melodies, harmonious journey, heart of theatre, intricate choreography, musical, operettas and vaudeville, rich history, sheer magic, stories told through song, transporting us, unique and immersive theatrical experience